
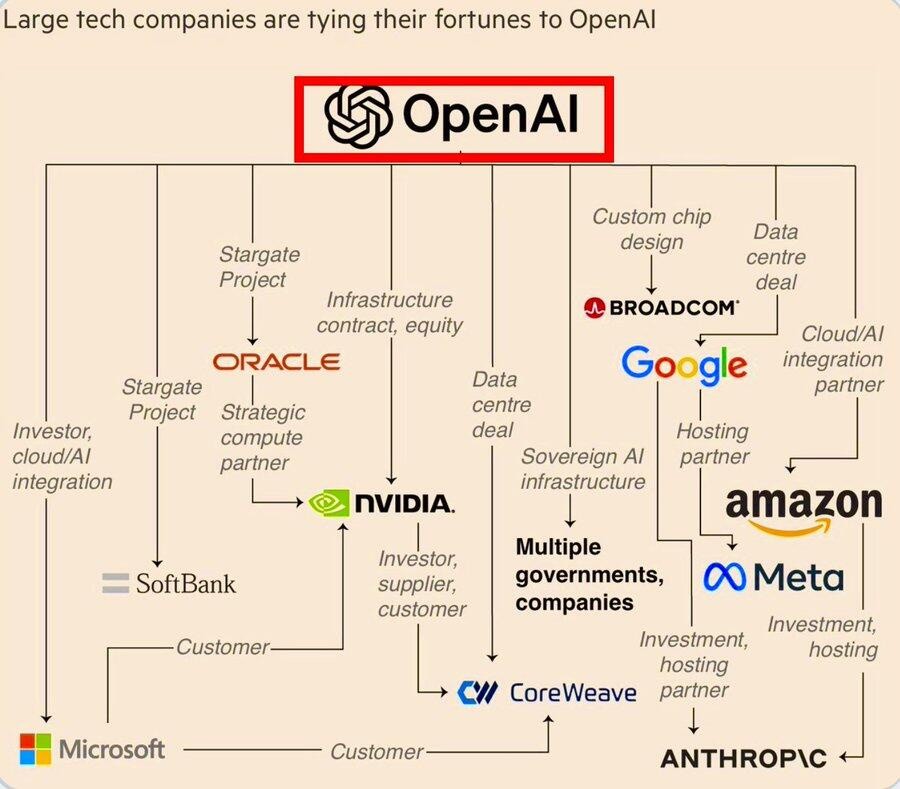
Collaborating with Broadcom to design AI chips and with Arm to design CPUs, stock prices surged, OpenAI once again demonstrated its "stock market Midas touch."

OpenAI's collaboration with Broadcom has driven its stock price up by 11%, and it has been reported that it is in talks with Arm to design AI server CPUs, which has again caused Arm's stock price to surge over 11%. This not only highlights OpenAI's ambitions in the chip sector but also underscores the key role that SoftBank, as its major shareholder, plays behind the scenes. This series of deep collaborations signals the formation of an "AI alliance," but it also comes with significant capital challenges
OpenAI's title as the "stock market golden hand" seems secure—whenever it collaborates, stock prices respond positively.
Overnight, OpenAI signed a multi-year agreement with Broadcom to deploy 10 gigawatts of AI data center capacity. Broadcom's stock price reacted immediately, soaring by 11%.
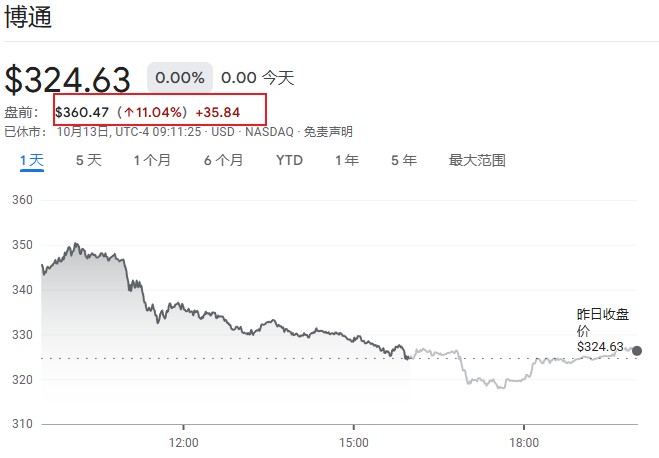
Following the disclosure of the collaboration with Broadcom, another key initiative from OpenAI came to light—deep discussions with Arm, the semiconductor design giant under SoftBank. On October 13, The Information cited informed sources stating that OpenAI is in talks with Arm to incorporate Arm-designed central processing units (CPUs) into AI server chips co-designed with OpenAI.
Furthermore, Arm hopes that OpenAI will also consider using Arm's CPUs when pairing with NVIDIA and AMD's AI chips. Subsequently, Arm's stock price surged over 11%, continuing to rise more than 6% in after-hours trading.
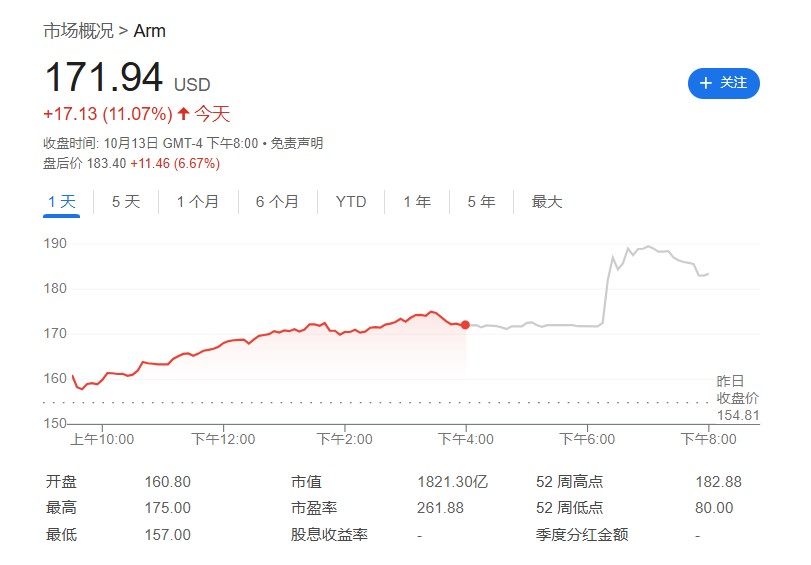
It is noteworthy that SoftBank, as one of OpenAI's largest shareholders, holds nearly 90% of Arm's shares. SoftBank has not only invested billions of dollars in OpenAI but has also committed to additional capital amounting to hundreds of billions to support its data center construction plans.
Additionally, a document obtained by the media indicates that SoftBank has committed to purchasing AI technology worth billions of dollars from OpenAI annually starting this year, some of which will be used to help Arm shorten the development time for new chips. This suggests that while OpenAI is advancing its own development, it is also creating significant commercial value for SoftBank and its affiliates, making SoftBank an important driver and beneficiary behind OpenAI's grand plans.
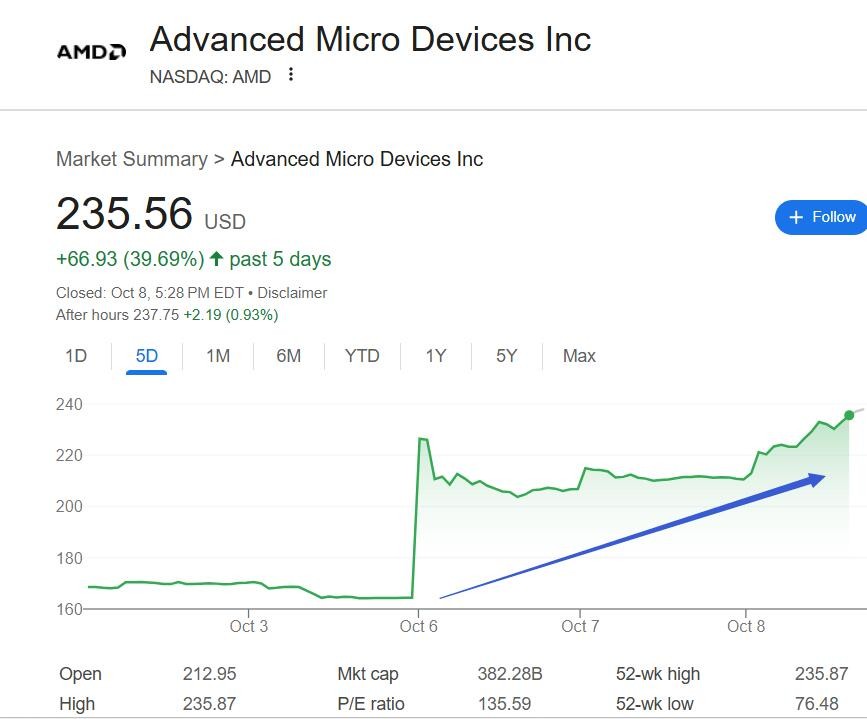
This is not the first time OpenAI has demonstrated its "stock market golden hand" magic. In previous collaborations with chip design company AMD, AMD surged 43% in three days.
With OpenAI's collaborations with Oracle, NVIDIA, and other giants, a close-knit "AI alliance" seems to have already taken shape.
Deep into the Chip Territory: Collaboration with Broadcom and Arm
OpenAI's chip strategy reflects a clear division of labor. The collaboration with Broadcom focuses on the AI chip itself, which is specifically designed for "inference"—that is, running AI models that have already been developed. Discussions with Arm center on the CPUs that support AI server chips. According to an insider, all AI chips need to work in conjunction with CPUs, and the CPU designed by Arm for OpenAI aims to handle more computational tasks than the current CPUs paired with NVIDIA chips.
It is noteworthy that for Arm, directly developing CPUs is a new business, as the company previously mainly sold chip design blueprints. According to an insider, this potential collaboration with OpenAI could bring Arm billions of dollars in potential revenue. Currently, OpenAI has not publicly disclosed its collaboration with Arm.
Supply Chain Game: Challenging NVIDIA and Competing for TSMC
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has stated that OpenAI aims to build 250 gigawatts (GW) of new computing capacity by 2033, which would cost over $10 trillion at current standards. To achieve this ambitious goal, OpenAI needs substantial financial support and seeks to reduce its reliance on a single GPU supplier.
The collaboration with Broadcom is aimed at producing chips specifically for AI inference, expected to be operational by the end of next year at the earliest, with the goal of providing chip support for 10 GW of data center capacity, which is about five times OpenAI's current usage capacity.
OpenAI President Greg Brockman pointed out that OpenAI has been collaborating with Broadcom on the chip project for 18 months. The idea for this custom chip originated a few years ago when OpenAI communicated with several chip startups and found that they "did not listen to our opinions," leading OpenAI to decide to develop the chips independently.
However, chip production cannot do without foundries. The chips designed in collaboration with Broadcom will be manufactured by TSMC, which is also the manufacturer for most AI chips from companies like NVIDIA and AMD.
To ensure production capacity, Altman recently met with TSMC executives to urge them to release more capacity. TSMC executives stated last year that they would be willing to expand chip production if OpenAI could commit to large orders.
The Capital Risks Behind the "Midas Touch"
These major transactions by OpenAI will involve enough chips to support 26 GW of data center capacity. According to The Information, the construction cost for this capacity will exceed $1 trillion based on current costs for building large data centers.
Wall Street Insight reported that Bloomberg columnist Matt Levine vividly pointed out that OpenAI's financing strategy is a form of "world-class financial engineering." He believes that through this massive procurement, OpenAI binds the fate of its suppliers to itself, thereby creating a mechanism where "money problems will solve themselves."
If you owe the bank $100, that's your problem. If you owe Broadcom $500 billion, that's Broadcom's problem. If you owe every major tech company hundreds of billions, that's their problem. They will definitely find a way to solve it! Or you will. The money problem will resolve itself.
Despite OpenAI generating about $13 billion in revenue this year, it is expected to burn through $115 billion in cash by 2029. Goldman Sachs analysis indicates that when accounting for future significant capital commitments, OpenAI's total funding needs will reach $114 billion by 2026, with 75% relying on external equity and debt financing. Under this model, OpenAI's dependence on external capital is astonishing


